|
| PINCHA EN LA IMAGEN Y VIAJA POR LA HISTORIA |
jueves, 15 de marzo de 2018
miércoles, 14 de marzo de 2018
viernes, 9 de marzo de 2018
Unidad 10: Longitud, capacidad y masa
Realiza los siguientes ejercicios y te resultará más fácil el tema
UNIDAD 7 : LA EDAD MEDIA
UNIDAD 7: LA EDAD MEDIA
TEMA 7 - LA EDAD MEDIA - "AL-ÁNDALUS""
ð Córdoba fue una de las ciudades más populosas e importantes de la época. Acogía brillantes médicos, poetas, astrónomos, filósofos y músicos.
ð Durante el califato de Córdoba (Abderramán III), al-Ándalus tuvo un gran desarrollo científico y cultural,
Iniciado el s. VII, en la Península Arábiga había surgido una nueva religión: el Islam. Hacia el año 620, en la Meca, Mahoma comenzó a predicar esta nueva religión que se extendería rápidamente por oriente y el norte de África. El Dios de los musulmanes (seguidores del Islam) se llama Alá y su libro sagrado es el Corán.
En el año 711, un ejército musulmán llegó desde África e invadió el reino visigodo, conquistando en pocos años, casi toda la península y las islas Baleares. Los musulmanes llamaron a este territorio al-Ándalus y establecieron su capital en Córdoba.
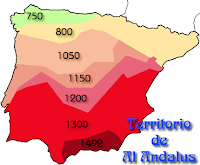
Al-Ándalus es el nombre que se dio al territorio de la Península Ibérica dominado por los musulmanes y que abarcó desde el año 711 hasta finales del siglo XV (1492). Su extensión variaba a medida que cambiaban las fronteras a causa de las continuas conquistas del territorio realizadas o bien por hispano-musulmanes, bien por castellano-aragoneses.
La mayoría de los habitantes de al-Ándalus adoptaron la religión musulmana, el idioma árabe y las costumbres musulmanas.
- Emir: gobernador de una provincia (emirato)
- Califa: Máxima autoridad, civil y religiosa, del mundo musulmán (califato)
Primero al-Ándalus fue un emirato dependiente del califa de Damasco, más tarde, el emir Abderramán III adoptó el título de califa e inauguró el califato de Córdoba que se prolongó hasta el año 1031. Durante este periodo, al-Ándalus llevó a cabo grandes conquistas militares (Almanzor), y tuvo un gran desarrollo científico y cultural, convirtiéndose Córdoba en una de las ciudades más populosas e importantes de la época. Acogía brillantes médicos, poetas, astrónomos, filósofos y músicos.
En el año 1.031, el califato se dividió en varios reinos más pequeños y débiles, enfrentados entre sí, que se denominaron taifas.
Para frenar el avance de los reinos cristianos, llegaron desde Africa nuevos ejércitos musulmanes: almorávides y, después, almohades.
En el año 1212, un ejército compuesto por castellanos, navarros y aragoneses derrotó a las tropas musulmanas en la batalla de las Navas de Tolosa, dejando solo Granada como territorio musulmán.
Esto fue un proceso largo (8 siglos) conocido como Reconquista:
(observa en el mapa, como evolucionan las fronteras)
El reino de Granada destacó por la belleza de sus construcciones, como la Alhambra y por su gran desarrollo cultural. Pero las luchas internas lo debilitaron y los Reyes Católicos lo conquistaron en 1492.
P A R A V E R
P A R A I N V E S T I G A R
A C T I V I D A D E S
P A R A Q U E R E C U E R D E S:
ð En el año 711, un ejército musulmán llegó desde África, derrotó al reino visigodo, conquistando casi toda la península.
ð Los musulmanes llamaron a este territorio al-Ándalus y establecieron su capital en Córdoba. ð Córdoba fue una de las ciudades más populosas e importantes de la época. Acogía brillantes médicos, poetas, astrónomos, filósofos y músicos.
ð Durante el califato de Córdoba (Abderramán III), al-Ándalus tuvo un gran desarrollo científico y cultural,
ð Desde el s. XI, al-Ándalus se disgregó en reinos de taifas, llegando de África los almorávides y almohades .
ð En 1492, los Reyes Católicos reconquistaron el último reino musulmán: Granadamiércoles, 7 de marzo de 2018
martes, 6 de marzo de 2018
UNIT 7: "The Middle Ages"
UNIT
7: THE MIDDLE AGES
The
Muslim invasion:
In
711, Muslims from North Africa invaded Visigoth Spain. After the
Battle of Guadalete,
in
which the Visigoths were defeated, Muslim armies continued the
conquest. In a few years
they
conquered most of the Iberian Peninsula and the Balearic Islands. The
Muslims called
their
conquered territory Al- Andalus.
Economy
and society:
There
were three religious groups: Muslims, Christians and Jews. Most of
the people in Al- Andalus lived in walled towns and cities. Their
main activities were crafts and trade. The medina (where craftspeople
lived) and the zoco were in the centre of the city. People prayed in
a
mosque (mezquita). There was usually a fort called an alcazaba
and fortified place called an
alcazar.
The cities were surrounded by fields were farmers grew cereals,
olives and grapes.
The
legacy of Al-Andalus:
The
Muslims gave a lot to Spain, specially their knowledge (medicine,
astronomy and
mathematics).
Stages
of the Reconquista:
Between
the 8th and the 10th centuries, the Christians form the north of the
Iberian Peninsula created small kingdoms that were independent of Al-
Andalus.
Don
Pelayo, the ruler of the Kingdom of Asturias defeated the Muslim army
at the Battle of
Covadonga.
This marked the beginning of the Reconquista.
In
the 11th century, Al-Andalus was divided into small independent
states called taifas and Alfonso VI, the king of León and Castilla,
conquered Toledo.
Soon,
the Christian Kingdoms united and became bigger and stronger.
In
1212, the forces of the Kingdoms of Aragón, Navarra, Castilla
and Portugal defeated the Muslims
at
the Battle of Las Navas de Tolosa. Soon, the kings of Castilla
conquered Andalucía.
In
1469, king Fernando II of Aragón and queen Isabel I of
Castilla married and united
their
two kingdoms.
In
1492, the Christians finally conquered the Kingdom of Granada.
Repopulation:
The
Reconquista involved not only the fighting, but also the repopulation
of areas previously occupied by the Muslims.
Feudalism:
It
was a hierarchical social system that was used in the Middle
Ages. It consisted of the king
and
four other groups of people:
1-
The king who ruled the country.
2
- The nobles who were very rich and lived in castles.
-
The knights who fought in the noble ́s armies and got land from
thems.
3
- The clergy who were religious people like priests, monks and
nuns.
4-
The peasants who were serfs. They had to work on the nobles ́ land
and give them part
of
their crops.
Medieval
cities:
They
were protected by a large wall. People had to enter and leave the
cities through fortified
gateways.
Streets were very narrow and people lived in bad conditions.
Crafts
people and artisans made products which were bought and sold by
merchants.
Craftspeople
who did the same type of work joined together to form guilds in order
to control
the
price and quality of the products.
In
the Middle Ages there were four main styles of medieval art in Spain:
Islamic, Romanesque, Gothic and Mudéjar.
Suscribirse a:
Comentarios (Atom)









.jpg)
.jpg)

.jpg)

.jpg)